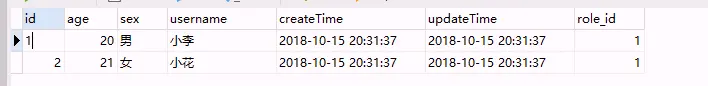
在我们开发一个新的功能的时候,会根据表创建Entity,Controller,Service,Repository等代码,其中很多步骤都是重复的,并且特别繁琐。这个时候就需要一个代码生成器帮助我们解决这个问题从而提高工作效率,让我们更致力于业务逻辑。设计原理
在我们安装数据库后会有几个默认的数据库,其中information_schema这个数据库中保存了MySQL服务器所有数据库的信息,如:数据库名、数据库表、表的数据信息与访问权限等。
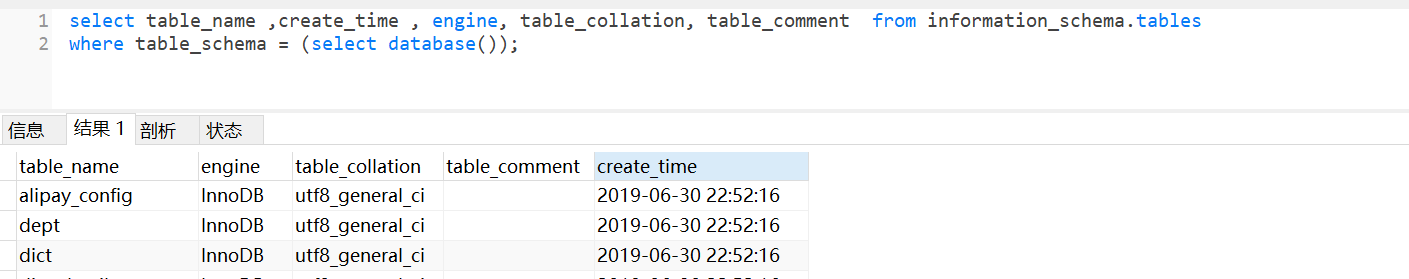
information_schema的表tables记录了所有数据库的表的信息
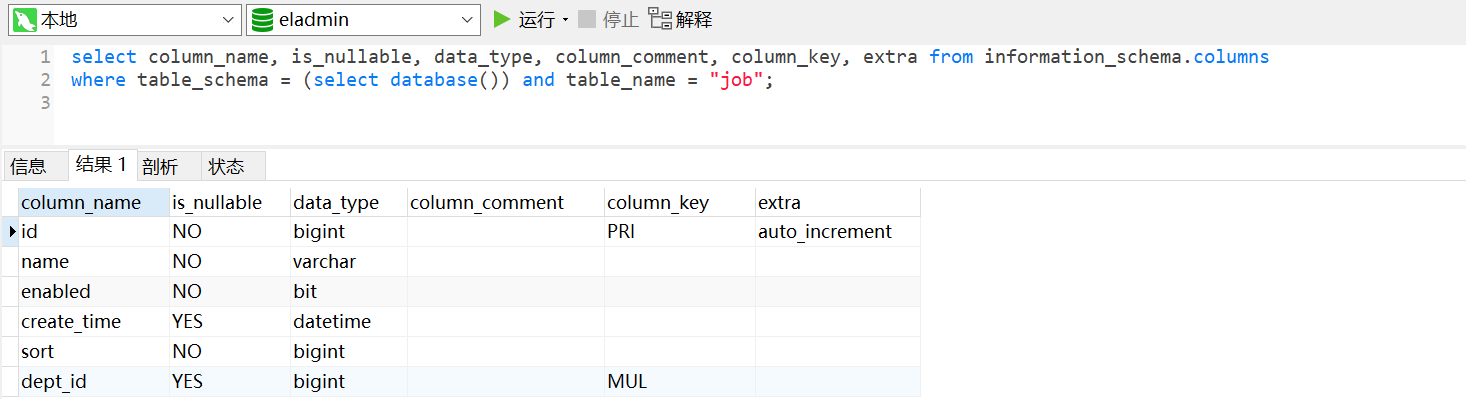
information_schema的表columns记录了所有数据库的表字段详细的信息
我们代码中可以可以通过Sql语句查询出当前数据库中所有表的信息,这里已 eladmin 为例。
# 显示部分数据:表名称、数据库引擎、编码、表备注、创建时间
select table_name ,create_time , engine, table_collation, table_comment from information_schema.tables
where table_schema = (select database());
知道表的数据后,可以查询出表字段的详细数据,这里用 job 表为例
sql语句如下:
# 显示部分数据:字段名称、字段类型、字段注释、字段键类型等
select column_name, is_nullable, data_type, column_comment, column_key, extra from information_schema.columns
where table_schema = (select database()) and table_name = "job";
有了表字段信息的数据后,通过程序将数据库表字段类型转换成Java语言的字段类型,再通过FreeMarker创建模板,将数据写入到模板,输出成文件即可实现代码生成功能。
代码实现
这里只贴出核心代码,源码可查询文末地址,首先创建一个新的spring boot 项目,选择如下依赖
Maven完整依赖如下
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 配置管理工具 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-configuration</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-configuration</artifactId>
<version>1.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
项目结构如下
教程开始
修改Spring boot 配置文件 application.yml,如下
service:
port: 8080
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eladmin?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jpa:
show-sql: true
在 resources 目录下创建 Mysql 字段与 Java字段对应关系的配置文件 generator.properties,生成代码时字段转换时使用
tinyint=Integer
smallint=Integer
mediumint=Integer
int=Integer
integer=Integer
bigint=Long
float=Float
double=Double
decimal=BigDecimal
bit=Boolean
char=String
varchar=String
tinytext=String
text=String
mediumtext=String
longtext=String
date=Timestamp
datetime=Timestamp
timestamp=Timestamp
在 vo 包下创建临时 Vo 类 ColumnInfo,该类的功能用于接收Mysql字段详细信息
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ColumnInfo {
/** 数据库字段名称 **/
private Object columnName;
/** 允许空值 **/
private Object isNullable;
/** 数据库字段类型 **/
private Object columnType;
/** 数据库字段注释 **/
private Object columnComment;
/** 数据库字段键类型 **/
private Object columnKey;
/** 额外的参数 **/
private Object extra;
}
在 util 包下创建字段工具类 ColumnUtil,该类的功能用于转换mysql类型为Java字段类型,同时添加驼峰转换方法,将表名转换成类名
import org.apache.commons.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.commons.configuration.ConfigurationException;
import org.apache.commons.configuration.PropertiesConfiguration;
/**
* sql字段转java
*
* @author jie
* @date 2019-01-03
*/
public class ColumnUtil {
private static final char SEPARATOR = '_';
/**
* 获取配置信息
*/
public static PropertiesConfiguration getConfig() {
try {
return new PropertiesConfiguration("generator.properties");
} catch (ConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 转换mysql数据类型为java数据类型
* @param type
* @return
*/
public static String cloToJava(String type){
Configuration config = getConfig();
return config.getString(type,null);
}
/**
* 驼峰命名法工具
*
* @return toCamelCase(" hello_world ") == "helloWorld"
* toCapitalizeCamelCase("hello_world") == "HelloWorld"
* toUnderScoreCase("helloWorld") = "hello_world"
*/
public static String toCamelCase(String s) {
if (s == null) {
return null;
}
s = s.toLowerCase();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s.length());
boolean upperCase = false;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (c == SEPARATOR) {
upperCase = true;
} else if (upperCase) {
sb.append(Character.toUpperCase(c));
upperCase = false;
} else {
sb.append(c);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* 驼峰命名法工具
*
* @return toCamelCase(" hello_world ") == "helloWorld"
* toCapitalizeCamelCase("hello_world") == "HelloWorld"
* toUnderScoreCase("helloWorld") = "hello_world"
*/
public static String toCapitalizeCamelCase(String s) {
if (s == null) {
return null;
}
s = toCamelCase(s);
return s.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + s.substring(1);
}
}
在 util 包下创建代码生成工具类 GeneratorUtil,该类用于将获取到的Mysql字段信息转出Java字段类型,并且获取代码生成的路径,读取 Template,并且输出成文件,代码如下:
import freemarker.template.Configuration;
import freemarker.template.Template;
import freemarker.template.TemplateException;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import java.io.*;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 代码生成
*
* @author jie
* @date 2019-01-02
*/
@Slf4j
public class GeneratorUtil {
private static final String TIMESTAMP = "Timestamp";
private static final String BIGDECIMAL = "BigDecimal";
private static final String PK = "PRI";
private static final String EXTRA = "auto_increment";
/**
* 生成代码
* @param columnInfos
* @param pack
* @param author
* @param tableName
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void generatorCode(List<ColumnInfo> columnInfos, String pack, String author, String tableName) throws IOException {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("package", pack);
map.put("author", author);
map.put("date", LocalDate.now().toString());
map.put("tableName", tableName);
// 转换为小写开头的的类名, hello_world == helloWorld
String className = ColumnUtil.toCapitalizeCamelCase(tableName);
// 转换为大写开头的类名, hello_world == HelloWorld
String changeClassName = ColumnUtil.toCamelCase(tableName);
map.put("className", className);
map.put("changeClassName", changeClassName);
// 是否包含 Timestamp 类型
map.put("hasTimestamp", false);
// 是否包含 BigDecimal 类型
map.put("hasBigDecimal", false);
// 是否为自增主键
map.put("auto", false);
List<Map<String, Object>> columns = new ArrayList<>();
for (ColumnInfo column : columnInfos) {
Map<String, Object> listMap = new HashMap<>();
listMap.put("columnComment", column.getColumnComment());
listMap.put("columnKey", column.getColumnKey());
String colType = ColumnUtil.cloToJava(column.getColumnType().toString());
String changeColumnName = ColumnUtil.toCamelCase(column.getColumnName().toString());
if (PK.equals(column.getColumnKey())) {
map.put("pkColumnType", colType);
map.put("pkChangeColName", changeColumnName);
}
if (TIMESTAMP.equals(colType)) {
map.put("hasTimestamp", true);
}
if (BIGDECIMAL.equals(colType)) {
map.put("hasBigDecimal", true);
}
if (EXTRA.equals(column.getExtra())) {
map.put("auto", true);
}
listMap.put("columnType", colType);
listMap.put("columnName", column.getColumnName());
listMap.put("isNullable", column.getIsNullable());
listMap.put("changeColumnName", changeColumnName);
columns.add(listMap);
}
map.put("columns", columns);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(Configuration.VERSION_2_3_23);
configuration.setClassForTemplateLoading(GeneratorUtil.class, "/template");
Template template = configuration.getTemplate("Entity.ftl");
// 获取文件路径
String filePath = getAdminFilePath(pack, className);
File file = new File(filePath);
// 生成代码
genFile(file, template, map);
}
/**
* 定义文件路径以及名称
*/
private static String getAdminFilePath(String pack, String className) {
String ProjectPath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator;
String packagePath = ProjectPath + File.separator + "src" + File.separator + "main" + File.separator + "java" + File.separator;
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(pack)) {
packagePath += pack.replace(".", File.separator) + File.separator;
}
return packagePath + "entity" + File.separator + className + ".java";
}
private static void genFile(File file, Template template, Map<String, Object> params) throws IOException {
File parentFile = file.getParentFile();
// 创建目录
if (null != parentFile && !parentFile.exists()) {
parentFile.mkdirs();
}
//创建输出流
Writer writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file), "UTF-8"));
//输出模板和数据模型都对应的文件
try {
template.process(params, writer);
} catch (TemplateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在 resources 的 template 目录下创建 framework 模板 Entity.ftl,代码如下:
package ${package}.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
<#if hasTimestamp>
import java.sql.Timestamp;
</#if>
<#if hasBigDecimal>
import java.math.BigDecimal;
</#if>
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @author ${author}
* @date ${date}
*/
@Entity
@Data
@Table(name="${tableName}")
public class ${className} implements Serializable {
<#if columns??>
<#list columns as column>
<#if column.columnComment != ''>
// ${column.columnComment}
</#if>
<#if column.columnKey = 'PRI'>
@Id
<#if auto>
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
</#if>
</#if>
@Column(name = "${column.columnName}"<#if column.columnKey = 'UNI'>,unique = true</#if><#if column.isNullable = 'NO' && column.columnKey != 'PRI'>,nullable = false</#if>)
private ${column.columnType} ${column.changeColumnName};
</#list>
</#if>
}
创建服务类 GeneratorService,该类用于获取数据库表的源数据
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import javax.persistence.Query;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 代码生成服务
*/
@Service
public class GeneratorService {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager em;
public List<ColumnInfo> getColumns(String tableName) {
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder("select column_name, is_nullable, data_type, column_comment, column_key, extra from information_schema.columns where ");
if(!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(tableName)){
sql.append("table_name = '").append(tableName).append("' ");
}
sql.append("and table_schema = (select database()) order by ordinal_position");
Query query = em.createNativeQuery(sql.toString());
List result = query.getResultList();
List<ColumnInfo> columnInfos = new ArrayList<>();
for (Object o : result) {
Object[] obj = (Object[])o;
columnInfos.add(new ColumnInfo(obj[0],obj[1],obj[2],obj[3],obj[4],obj[5]));
}
return columnInfos;
}
}
由于没有前端页面,所以只能在测试类中演示代码生成功能,GeneratorDomeApplicationTests 修改如下
import com.ydyno.util.GeneratorUtil;
import com.ydyno.vo.ColumnInfo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class GeneratorDomeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private GeneratorService generatorService;
@Test
void genTest() throws IOException {
String tableName = "job";
String pack = "com.ydyno";
String author = "Zheng Jie";
List<ColumnInfo> columnInfos = generatorService.getColumns(tableName);
GeneratorUtil.generatorCode(columnInfos,pack,author,tableName);
}
}
执行后,查看创建好的Entity
]]>